Ransomware and malware are commonly confused, however they are different entities. Malware is a broad category that encompasses all types of harmful software, including ransomware. Essentially, all ransomware falls under the category of malware, but not all malware is ransomware. Threatware is a more extensive term that encompasses various malicious programs like spyware, ransomware, worms, and keyloggers.
To understand the differences between ransomware and malware, it is essential to delve deeper into the nuances of these two types of cyberattacks. This article will provide an overview of what ransomware and malware are, the differences between them, and how to protect against them.
Key Takeaways
- Malware is a general term that includes ransomware.
- Ransomware is a specific type of malware that encrypts data and demands a ransom payment.
- Protecting against ransomware and malware requires a combination of proactive measures and reactive responses.
What Is Malware?
Malware is a term used to describe any type of malicious software. Malware can take many forms, including viruses, trojans, worms, rootkits, spyware, adware, and ransomware. Malware is designed to create damage to a computer, network, or server. It can be spread through various means, such as visiting suspicious websites, downloading unreliable applications, or even physical access to a computer.
Malware is a type of malicious software that can harm your computer, steal your data, or damage your system. Trojan horses and cryptojacking are two common types of malware that trick users into executing malicious code or use their computer to mine cryptocurrency. Viruses and worms are designed to spread from one computer to another, while rootkits give unauthorized access to a computer. Adware and spyware are types of malware that display ads or collect user information without their knowledge, while spam bots can perform malicious tasks like spreading spam or directing web traffic as part of a DDoS attack.
One of the most dangerous forms of malware is ransomware, which encrypts a user’s files and demands a ransom for their release. Ransomware can be spread through various means, such as phishing emails, malicious websites, or even physical access to a computer.
It is important to note that the difference between malware and malicious code is subtle, and malicious code can include website scripts that exploit vulnerabilities to upload malware. While some forms of malware are relatively innocuous, others like ransomware can be extremely dangerous. It is crucial to take necessary measures to protect your computer from malware attacks, such as using antivirus software and avoiding suspicious links or downloads.
What Is Ransomware?
Ransomware is a type of malware that encrypts a victim’s files and systems, rendering them inaccessible to the victim. Threat actors then demand payment in exchange for restoring access to the files. Ransomware attacks can be launched in various ways, with phishing being one of the more common methods. Threat actors can disguise themselves as legitimate corporations or colleagues, tricking the victim into clicking a suspicious link or attachment.
A ransomware attack typically involves multiple stages, including escalating privileges to gain admin account permissions, executing files, exfiltrating data, and finally deploying the ransomware. Threat actors can also disguise themselves as a government agency or other authority, claiming that the system is locked down for security reasons.
The stages of a ransomware attack are depicted in the following:
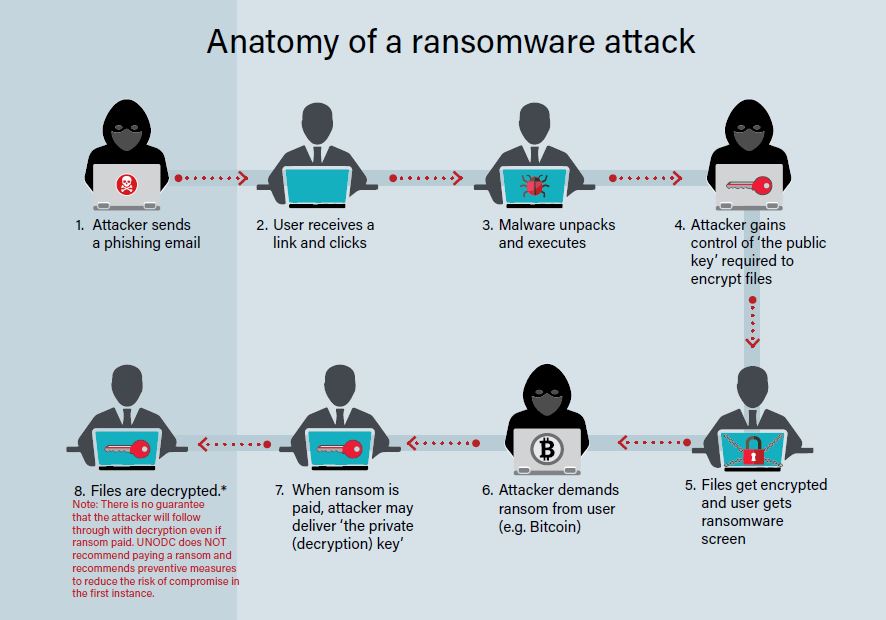
Overall, ransomware attacks can be devastating to individuals and organizations alike, and it is crucial to take steps to prevent them from occurring.
Types of Ransomware
Ransomware is a type of malware that encrypts a victim’s data and demands a ransom payment in exchange for the decryption key. There are several types of ransomware, and each operates differently. Here are some of the most common types of ransomware:
Crypto Ransomware
Crypto ransomware, also known as encryptors, is one of the most well-known and damaging variants. This type encrypts the files and data within a system, making the content inaccessible without a decryption key. The victim is then prompted to pay a ransom to obtain the key.
Locker Ransomware
Locker ransomware is a form of malware that will effectively prevent the victim from accessing their computer or network. It has the potential to lock the victim out of accessing everyday tools and computer applications until a ransom is paid.
Scareware
Scareware is a type of ransomware that tricks the victim into thinking their computer is infected with a virus or other malware. The victim is then prompted to pay a fee to have the supposed virus removed.
Doxware
Doxware, also known as leakware, is a type of ransomware that threatens to publish the victim’s sensitive information unless a ransom is paid. This type of ransomware is particularly damaging as it can expose the victim to identity theft and other forms of cybercrime.
Mobile Ransomware
Mobile ransomware targets mobile devices, such as smartphones and tablets, and typically operates in a similar manner to other types of ransomware. It can be spread through malicious apps or phishing attacks and can lock the victim out of their device until a ransom is paid.
Ransomware is a dangerous type of malware that can cause significant harm to victims. Therefore, understanding the different types of ransomware can help individuals and organizations better protect themselves against these threats.
See also: What Is An SSL certificate? And How Does it Works?
What’s The Difference Between Ransomware and Malware?
Ransomware and malware are both malicious software, but there are some key differences between the two. The chart below highlights some of the main differences:
| Characteristic | Ransomware | Malware |
|---|---|---|
| Spread Technique | Typically spreads through deceptive attachments in phishing campaigns. | Distributed via multiple channels: malicious links, deceptive emails, rogue app downloads, and infected USBs. |
| Removal Complexity | Highly challenging; affected users are either compelled to pay a ransom or use a verified backup. | Removal is comparatively easier; common antivirus programs can handle most threats. |
| Types | Primarily restricted to encryption-based (crypto) and system-locking (locker) types. | Encompasses a broad spectrum: trojans, worms, spyware, adware, viruses, and more. |
| Consequences | Causes drastic impact; many organizations halt operations after a ransomware breach. | Varied effects; while some malware strains just slow down systems, others can exfiltrate data without disruption. |
| Main Objective | Primarily focuses on monetary extortion from victims by denying access to their data. | Diverse objectives: from data theft and spying to system disruption and unauthorized advertisements. |
The key differences between ransomware and other malware include the fact that ransomware is typically spread through phishing emails or malicious downloads, and it is designed to encrypt files and demand payment in exchange for the decryption key. In contrast, other forms of malware may be spread through a variety of methods, such as exploiting vulnerabilities in software or using social engineering tactics to trick users into installing the software. Additionally, other forms of malware may be designed to steal data or cause damage to systems without demanding payment.
The impact of ransomware is often severe and long-lasting. Many businesses have shut down operations due to ransomware attacks. While commodity malware can control data and resources and reduce system performance, it generally doesn’t destroy a business.
How To Protect Against Ransomware or Malwares?
Ransomware and malware attacks can be devastating for both individuals and organizations. Here are some ways to protect yourself against these types of attacks:
- Keep your software up to date: Regularly update your operating system, antivirus software, and other applications to ensure that they are protected against the latest threats.
- Use strong passwords: Use strong, unique passwords for all of your accounts and change them regularly.
- Avoid suspicious emails and links: Don’t open email attachments or click on links from unknown sources. Be wary of emails that ask for personal information or contain urgent requests.
- Back up your data: Regularly back up your important files to an external hard drive or cloud storage service. This will help you recover your data in case of a ransomware attack.
- Use anti-malware software: Install reputable anti-malware software on your computer and keep it up to date.
- Be cautious when downloading software: Only download software from reputable sources. Avoid downloading software from pop-up ads or suspicious websites.
- Use a firewall: A firewall can help prevent unauthorized access to your computer or network.
- Educate yourself: Learn about the latest threats and how to protect yourself against them. Stay informed about the latest security updates and best practices.
By following these tips, you can help protect yourself against ransomware and malware attacks. Remember to always be vigilant and cautious when using your computer or mobile device.
See also: Public Wi-Fi Risks: Safety Measures and User Insights
Final Thoughts
Ransomware distinguishes itself within the malware universe with its specific aim: monetary extortion. This is achieved by encrypting victims’ data and seeking payment for its return, setting it apart from other malware types. It often spreads through phishing emails or harmful websites, but like other malware, it can also exploit software vulnerabilities.
Effective defenses against ransomware and malware in general encompass the use of strong passwords, consistent software updates, and frequent antivirus scans. Grasping and countering ransomware threats necessitates an active stance on cybersecurity and constant vigilance towards potential phishing tactics. By embracing these strategies, the risk from ransomware and other harmful software can be substantially reduced for both individuals and organizations.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are some examples of malicious software?
Malicious software, also known as malware, includes a variety of harmful programs that can infect a computer or network. Some common types of malware include viruses, worms, trojans, spyware, and adware. These programs can be used to steal sensitive information, damage or destroy files, and even take control of a computer remotely.
What is the difference between ransomware and other types of malware?
Ransomware is a specific type of malware that is designed to encrypt a victim’s files and demand payment in exchange for the decryption key. Unlike other types of malware, ransomware is focused on financial gain rather than data theft or destruction. Ransomware can be spread through email attachments, malicious websites, and infected software.
How can you tell if your computer has been infected with ransomware or malware?
There are several signs that your computer may be infected with ransomware or malware. These include slow performance, frequent crashes or freezes, unexpected pop-up windows, and unexplained changes to files or settings. If you suspect that your computer has been infected, it is important to run a virus scan and take steps to remove the malware as soon as possible.
What are some common examples of ransomware attacks?
Some common examples of ransomware attacks include WannaCry, Petya, and Locky. These attacks have affected individuals and organizations around the world, causing significant financial losses and disruptions to operations. Ransomware attacks can target any type of organization, from small businesses to large corporations and government agencies.
What are the potential consequences of a ransomware or malware attack?
The consequences of a ransomware or malware attack can be severe. In addition to financial losses, these attacks can lead to the theft or exposure of sensitive data, damage to critical systems, and loss of productivity. Ransomware attacks may also result in reputational damage and legal liabilities for affected organizations.
How can you protect your computer from ransomware and malware?
To protect your computer from ransomware and malware, it is important to keep your software up to date, use strong passwords, and avoid downloading software or opening email attachments from unknown sources. It is also recommended to use antivirus software and to regularly back up important files to an external device or cloud storage service. Additionally, organizations should implement security policies and training programs to educate employees on best practices for preventing ransomware and malware attacks.
